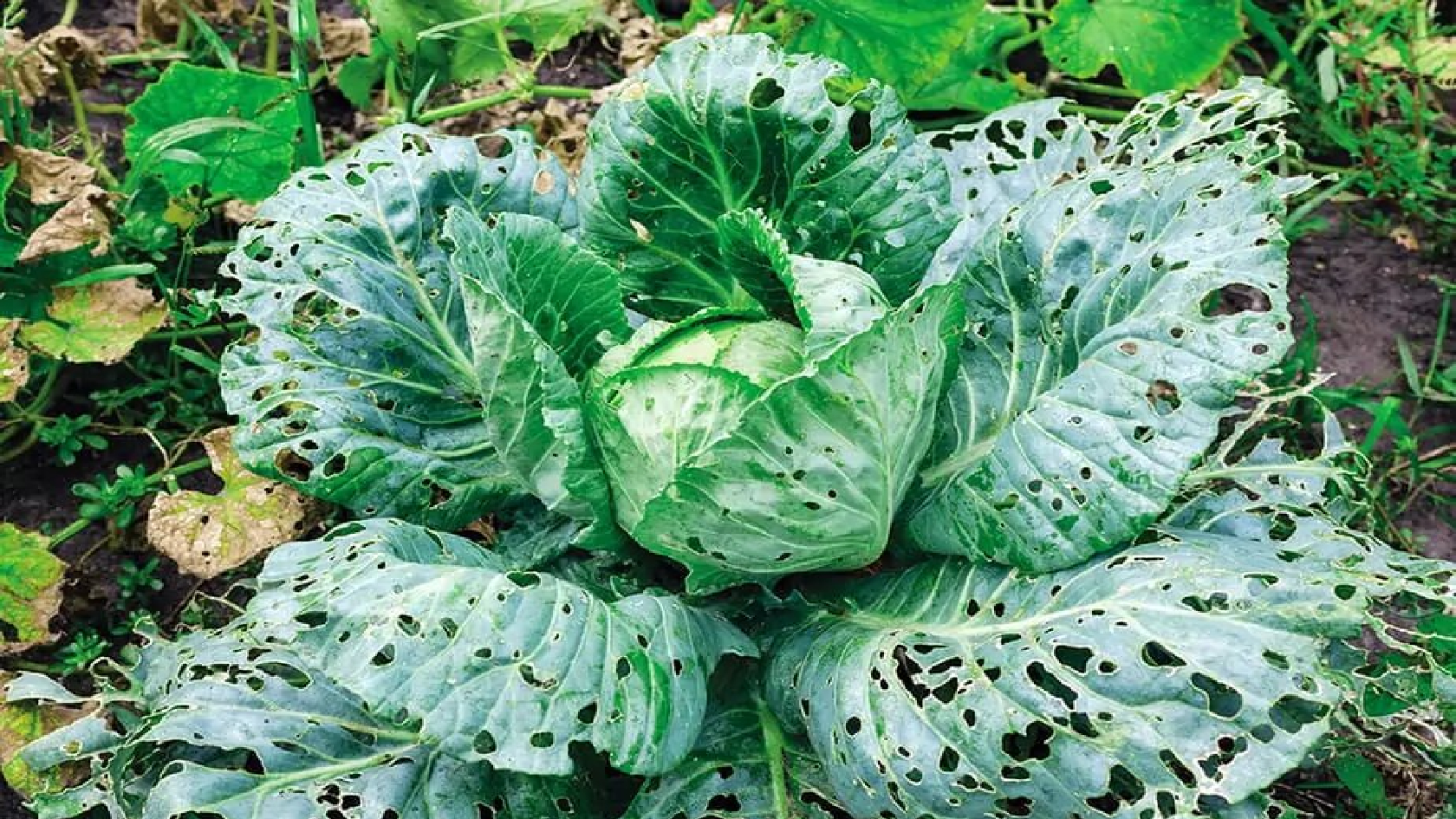
The nutritional characteristics of leaf vegetables are not only appreciated by humans but also by many other species. Achieve the best physical and nutritional conditions for your plants using i-Plant Nutrition and take care of their health. Here we present to you some important pests and diseases you can find in your crops. 1. Which species are considered leaf vegetables Leaf vegetables concert a big group of crops whose leaves are eatable as a vegetable. For example spinach, lettuce, silverbeet, Brussel sprouts, cabbage, kale, watercress, herbs, microgreens and salad greens, belongs to this group. They are commonly known as greens, but they are also described by different names such as leafy greens, salad greens, pot herbs or vegetable greens.
In general, they have especially in common its nutritional quality, providing great health benefits. They are full of vitamins and minerals, as well as being highly rich in fibre. They are used worldwide with a remarkable improvement of packing and storage methods that enables us to keep them fresh for up to six months, preserving their nutritional properties. However, since the consumable part is not protected by a shell, pests and diseases affect dramatically from the first day of the interaction. Because of that, we highly recommend you to find in this article some of the most common problems you can find in your leaf vegetable crop and put your efforts into preventing them. Of course, we encourage you to share with our community and experts any problem you find in your plants and your thoughts related to this topic.
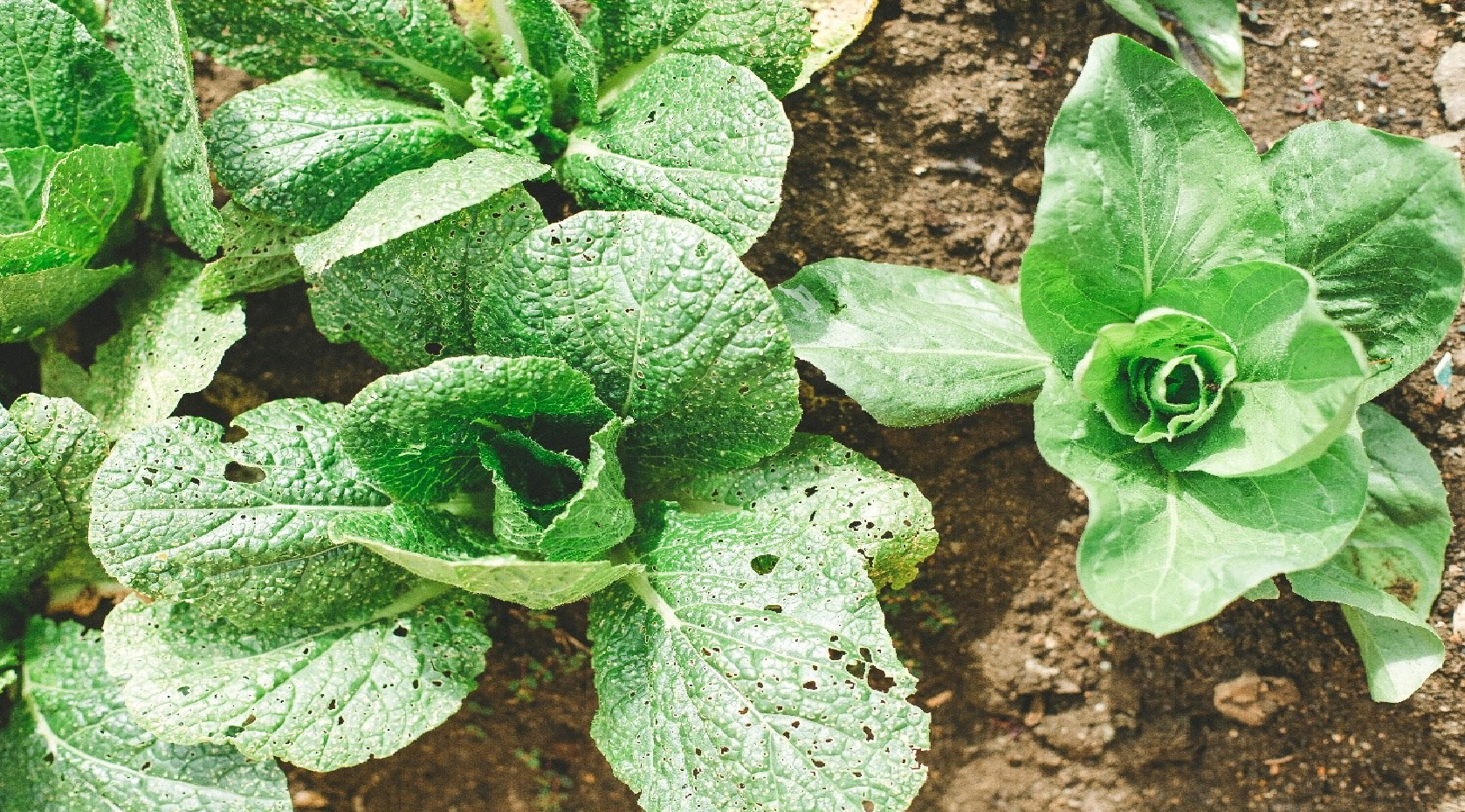

Leaf vegetable showing leaves damage. Image: Markus Spiske
2. The most common pests and diseases Even if many different plant species belong to this group, we can also cluster the most common pests and diseases they suffer, in order to understand the preferences of the different pathogens and try to prevent them. In addition, at i-Plant Nutrition you can obtain a personalized fertilization plan for your field, so your leaf vegetables get the necessary amount of nutrients to grow strong and healthy. 2.1. Insects find in these leaves all they need The leaves of these vegetables are highly appreciated all over the world cuisine. However, its juiciness is also highly appreciated by insects. For example, aphids have a preference for hosting the nerve of the leaves, from which they suck their juices. Infected leaves will eventually bleach and have stunted growth. Aphids can be seen with the naked eye and will sometimes be accompanied by a sticky residue called honeydew that they produce themselves. Try to eliminate them as soon as possible after they are observed because their reproduction rate is very high and rapidly a small problem with them will turn into a big infection.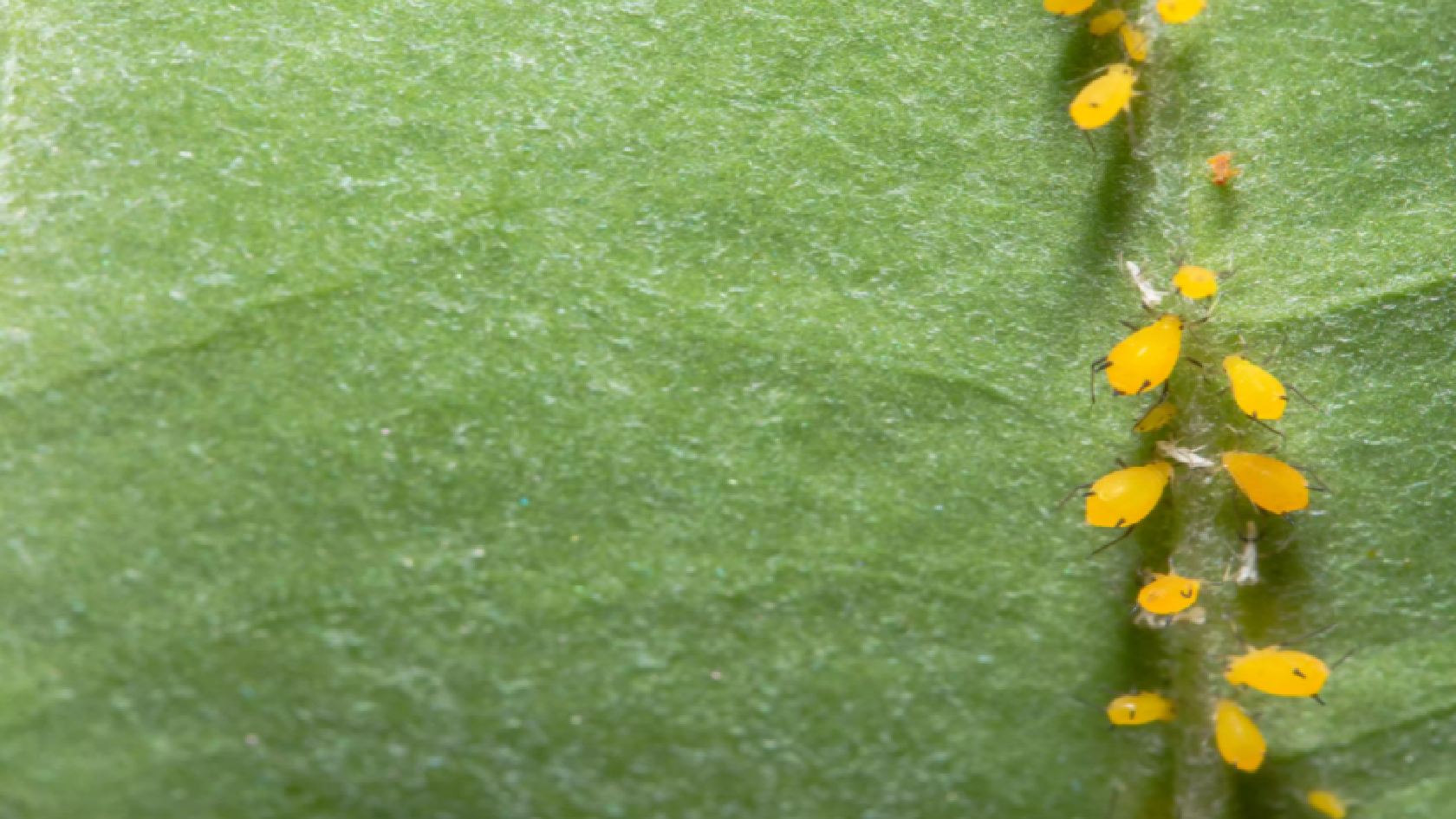
Aphids infecting a leaf. Aukid Phumsirichat / Getty Images
Sometimes we see uneven holes, different from the ones known as “shot holes” that bacteria form. These can be caused by insects. One of the most common ones is Pieris rapae. It is a white butterfly that let its eggs in the leaf vegetable. From those eggs, small green worms hatch and use the leaves as their main meal for all the caterpillar stage. These worms are so voracious that only a few of them can cause lethal damage to your plants. 2.2. The perfect environment for fungus For fungus to develop nutrients, warm temperature and humidity are essential. Luckily for them, they can find it all in vegetable plants. This makes a large number of fungi responsible for causing irreparable damage not only to the leaves but also to the roots of leaf vegetables.
In this article, we want to highlight Alternaria brassicae that causes Alternaria leaf spot disease. As its common name suggests, brown to black circular spots are formed in the leaves that enlarge forming concentric rings. The best way to get rid of this fungus is to burn the infected plants before spores get formed on them and spread to plants nearby. Applying fungicide immediately after seeing the symptoms is also effective, so make sure you keep a thorough track of your plant health status continuously.
The same procedures can be carried out to get rid of Pseudocercosporella capsellae, which is also a fungus that produces spots on leaves but is lighter in colour than Alternaria. It can survive on the plant seeds, so it can keep infecting the next generations. 2.3. Bacteria also want their part We just mentioned the leave spots formed by fungus. However, that is not exclusive of this kingdom. When we observe dark spots on leaves, they can also be caused by bacteria like Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas species. Compared to fungus, in those cases, the spots are water-soaked and will leave “shot holes” after they dry. So far, an effective cure for plants infected with bacterial spots does not exist, but you can try to prevent it by tracking the plants status periodically. 3. A general overview The nutritional characteristics of leaf vegetables are not only appreciated by humans but also by many other species. A large number of your plants can be wasted after harvesting if they do not show to be healthy enough to be commercialized. To get them at their best nutritional and physical conditions, use the i-Plant Nutrition to provide your crop with the fertilization they require and make sure you prevent any kind of pest and disease as soon as possible.