Is climate change something we can obviate? The truth is that those unstoppable changes are not only a prediction but also observed nowadays. Since we are facing the consequences, in this article you will find what are we expecting worldwide for the near future and what are the tools that may help us to generate a sufficient amount of food for this and next generations. 1. CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON GLOBAL AGRICULTURE Thanks to the detailed recording of meteorological phenomena, the strong trends that climate change is causing are already evident nowadays. Agriculture will have to adapt to continue generating sufficient amounts of food and to avoid future problems, an assessment of resource allocation, specific diversification of production systems and livelihoods is advised.
One of the factors that cause climate change is the exponential growth of CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This is largely due to human behaviour and is affecting both agriculture and forestry, as well as human health, biodiversity, snow cover, and aquatic and mountain ecosystems.
For this reason, Dr Meinke's group and his team in the article “Adapting agriculture to climate change” consider crucial the implementation of adaptation assessment frameworks that are relevant, robust and easily operated by all stakeholders, professionals, policy formulators and scientific professionals. 2. WHAT CAN WE NOTICE SO FAR? It is already well known that climate change causes erratic weather patterns, extreme temperatures and changes in natural resources. This affects crops gradually, more and more seriously. Those are the main reasons, being some of them even observable nowadays:
• Increases in periods of the year with excessive heat. This not only reduces the surface water but also affects the depletion of the aquifers. There are serious changes in pollination since the flowering of crops is interrupted. In addition, it increases the presence of weeds, insects and diseases.
• With regard to this, the presence of droughts that causes poor harvests and loss of arable land.
• On the other hand, excessive rainfall directly increases the risk of specific floods and damage to crops.
• All these changes lead to the elimination of habitats and foods for beneficial insects, for example pollinators, seed dispersers and decomposers of soil organic matter.
• Appearance of new pests and diseases, along with increased competition for soil and water sources. This increases the damage that external factors can do to crops.
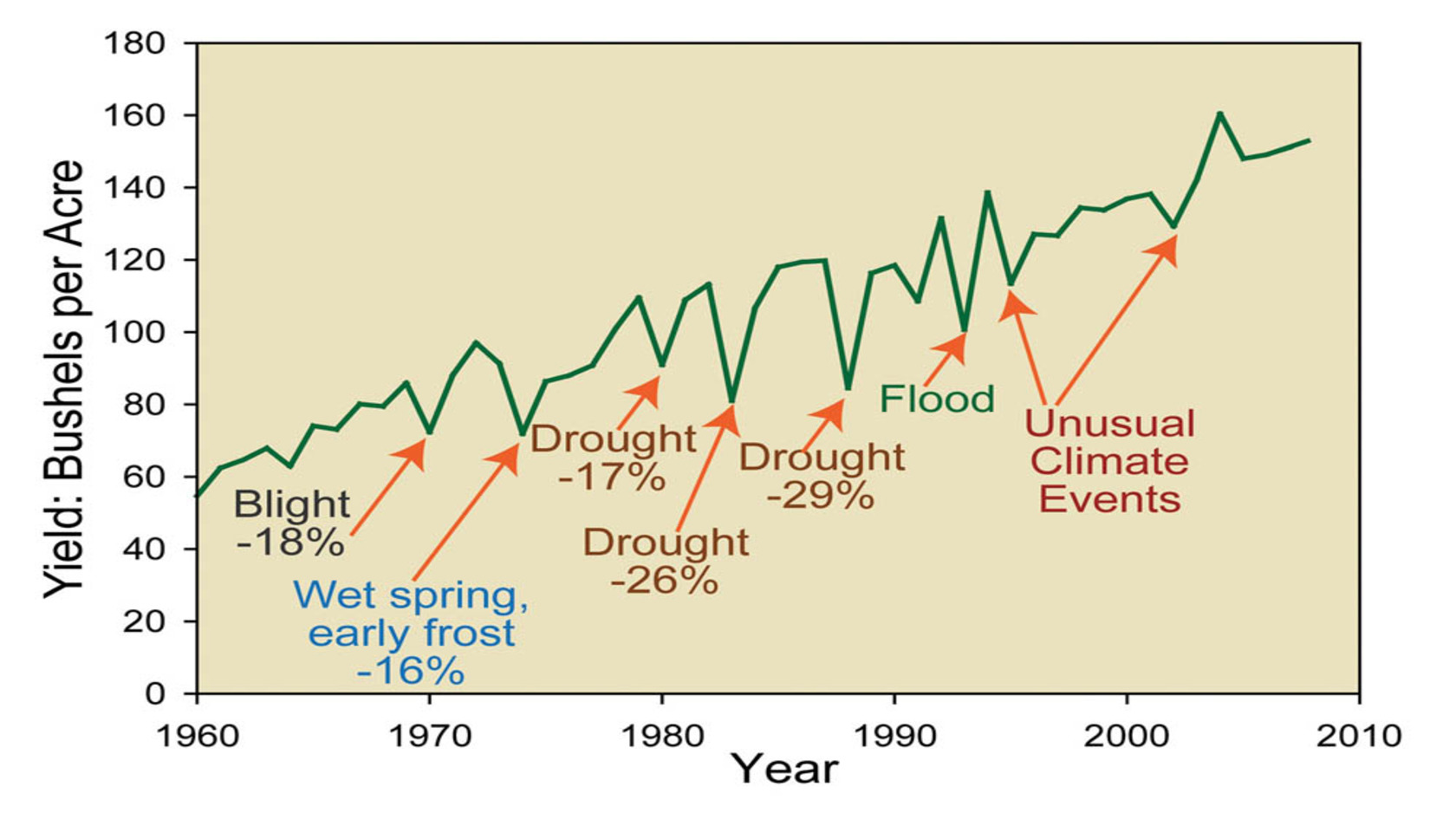
Image: Representation of corn yield and how some extreme weather events coincide with clear yield reductions.
This occurs despite technological improvements that help increase the yield of the corn. Source: USGCRP (US Global Change Research Program) 2009
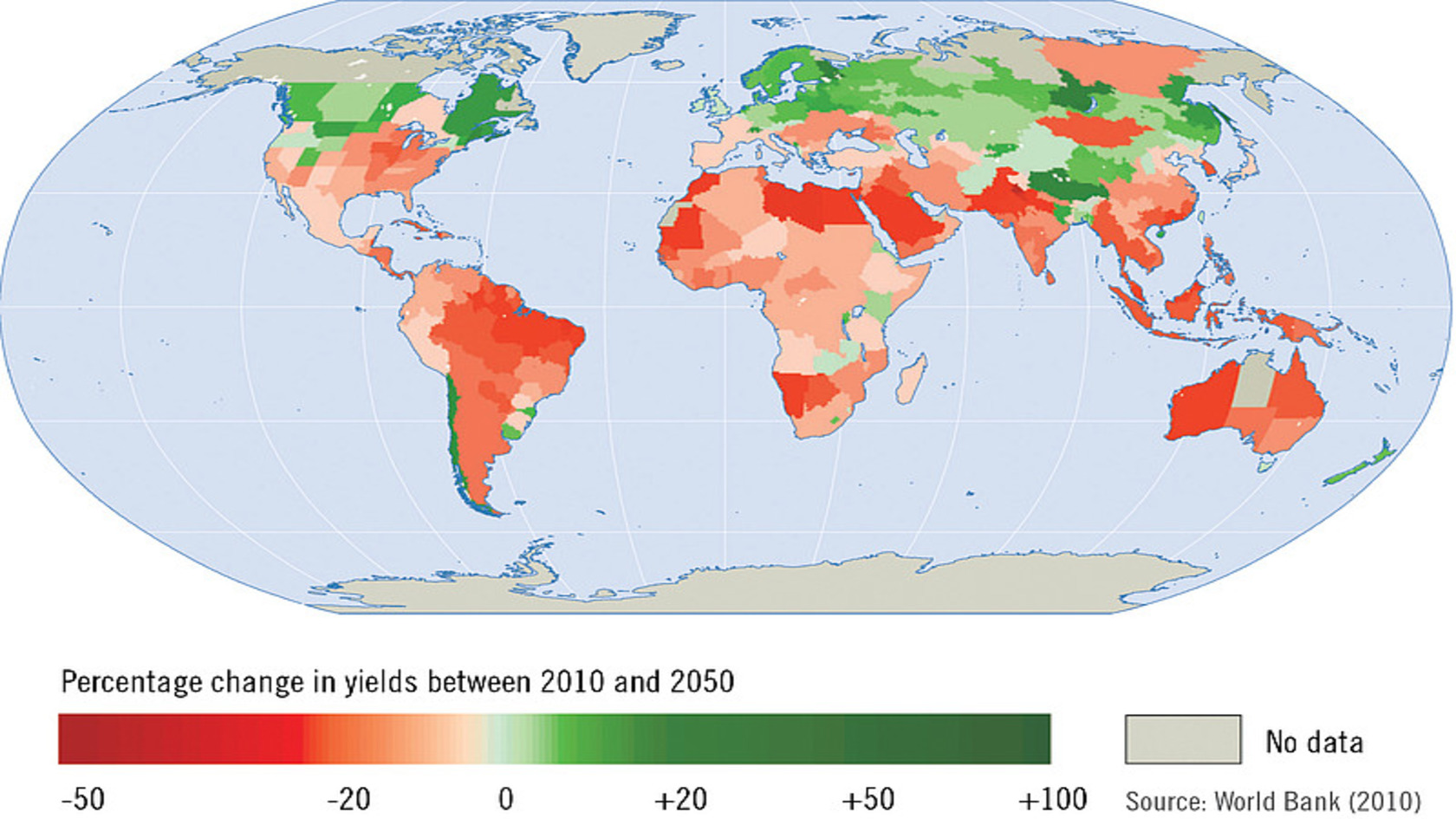
3.WHAT TOOLS WILL HELP ADAPTATION As climate change is not something we can obviate, it is smart to start devising tools that will help our crops survive despite the new conditions. For instance:
• Developing cropping systems strategies, such as the use of several crops growing at the same time. In periods of high water and/or thermal stress, this can help the systems to have greater durability.
• Research for crop improvement and development of new varieties of climate tolerant crops. This is a key tool for adapting agriculture to a changing climate. The natural biodiversity of crops allows the adaptation of plants to different conditions, however, scientific research is necessary for the development of plants with greater potential for adaptation to climate change.
At i-Plant Nutrition, we are concerned about the responsibility of human behaviour in climate change. That is why we offer in our software the best advice not only to reduce expenses in fertilizer applications but also to help farmers to take care of the environment.