HOW NUTRIENTS GET IN TOUCH WITH THE
ROOTS
Some people say that they feed the plants with fertilizer. That statement isn’t completely correct,
since plants aren’t actually fed by nutrients, instead, they “drink” them. Before the nutrients have any
sort of contact with the roots, they need to get into the soil solution, the liquid part of the soil
made of an electrolyte solution.
HOW NUTRIENTS GET IN TOUCH WITH THE
ROOTS
Some people say that they feed the plants with fertilizer. That statement isn’t completely correct,
since plants aren’t actually fed by nutrients, instead, they “drink” them. Before the nutrients have any
sort of contact with the roots, they need to get into the soil solution, the liquid part of the soil
made of an electrolyte solution.
Once they are in the soil solution, there are 3 ways for them to get in touch with the roots: Diffusion In this case, ions in their stationary phase present in the soil solution reach the root by a concentration gradient. In other words, the ion concentration by the roots is lower than in the soil solution, so the nutrients go towards the less concentrated region. When the ion content in the root gets high, the nutrients, once again by diffusion move to the aerial parts, decreasing the concentration in the roots, making the system start all over again.
This is the way phosphorous and potassium encounter the roots, it is a slow process and can only happen for nutrients that are less than 10 mm away from it. It is important to understand these contact mechanisms because they will dictate how well nutrients are absorbed by the crops. For instance, once we know that phosphorous contacts the root by diffusion, and also that it is a nutrient with low soil mobility, it is safe to assure that the absorption rate will be higher if phosphorous fertilizers are applied directly on the planting line or pit instead of broadcasted. Mass flow The water in the soil that will be absorbed by the plants carries the nutrients dissolved in the soil solution to the root surface. Mass flow is the main contact mechanism for most of the essential nutrients. It is a fast process and the quantity of nutrients that will get in touch with the root is proportional to the amount of water that gets there.
In order for this movement to happen, plant transpiration must happen as well. Once nutrients with high mobility in the soil (such as nitrogen, sulfur, calcium and magnesium) contact the root by mass flow, transpiration creates a potential gradient, allowing the nutrients to be absorbed. Root Interception This is the less usual way of nutrients to reach the roots’ surface, but it is still worth mentioning. Whenever the roots are developing and growing, they explore the soil in every direction and end up reaching nutrients present in the liquid and also in the solid phases of the soil. For this mechanism, it is important to know the size of the crop’s root system. MODES OF ROOT UPTAKE The nutrients from the fertilizer you applied are now in direct contact with the roots’ surface due to one of the mechanisms discussed above. It’s time for them to move inside the plant.
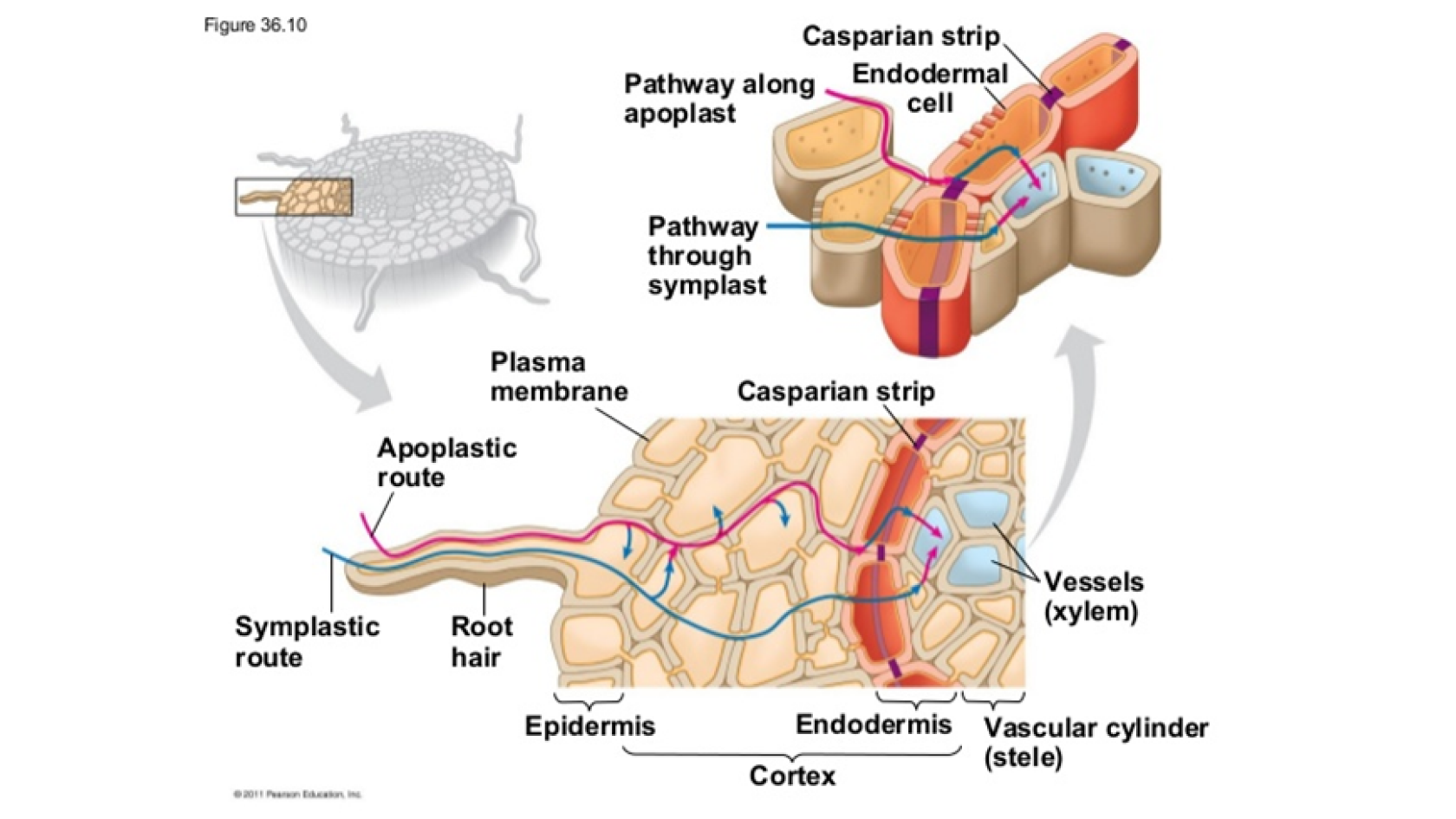
Once the ions reach the root, they have two different pathways to be absorbed:
The symplastic pathway is the slowest one. In this case, the ions are absorbed in the root surface and move towards the xylem from one cell interior to the other, having to cross the plasma membrane of each cell via cytoplasmic channels that connect them.
The ions can also take the fastest way, and go towards the xylem through the apoplastic pathway. This means that whenever they hit the root surface, they will move internally in the plant outside the cells, along the cell walls and extracellular space. Whenever they get to the endodermis, the Casparian strip won’t let them move forward through the apoplast, forcing it to be absorbed into the cell.
Now that the nutrient was absorbed and is already in the plant xylem, it will be translocated to another organ, usually the leaves. This movement can happen through transpiration (the plant loses water to the environment, creating a pressure gradient, moving water and nutrients towards the top of the plant), or if it’s a short distance transport, through cohesion and adhesion of the nutrients to the xylem walls.
This is the way the nutrients go from the fertilizer package to the plants’ leaves. Since you are now familiar with the whole process, you should let the i-Plant Nutrition assist you in creating the perfect fertilization plan for your crop, allowing you to save money and increase your yields!