It consists basically of the visual assessment of a plant, considering and comparing characteristics, such as size, shape and colour, and raising red flags for possible variations over the fields.
This evaluation can occur by analyzing the whole plant, or more specific parts, like the stem or the leaves, the last one being the organ with the highest metabolism, becoming very sensitive to nutritional variations, and therefore is usually where the symptoms are more pronounced.
The method of visual diagnosis of plant nutrition lies in the identification of symptoms patterns related to the role of each nutrient in the plant. Consequently, it is necessary to know the nutrient’s function and its mobility in the plant, because, in case of deficiency, nutrients with high mobility in the plant will move from the old leaves to the new ones in an attempt to save them, and as a result, the signs of nutrient deficiency will be shown on the old leaves. On the other hand, nutrients that are immobile in the plant won’t be able to move towards the new organs, causing the deficiency symptoms to be spotted on the old leaves.
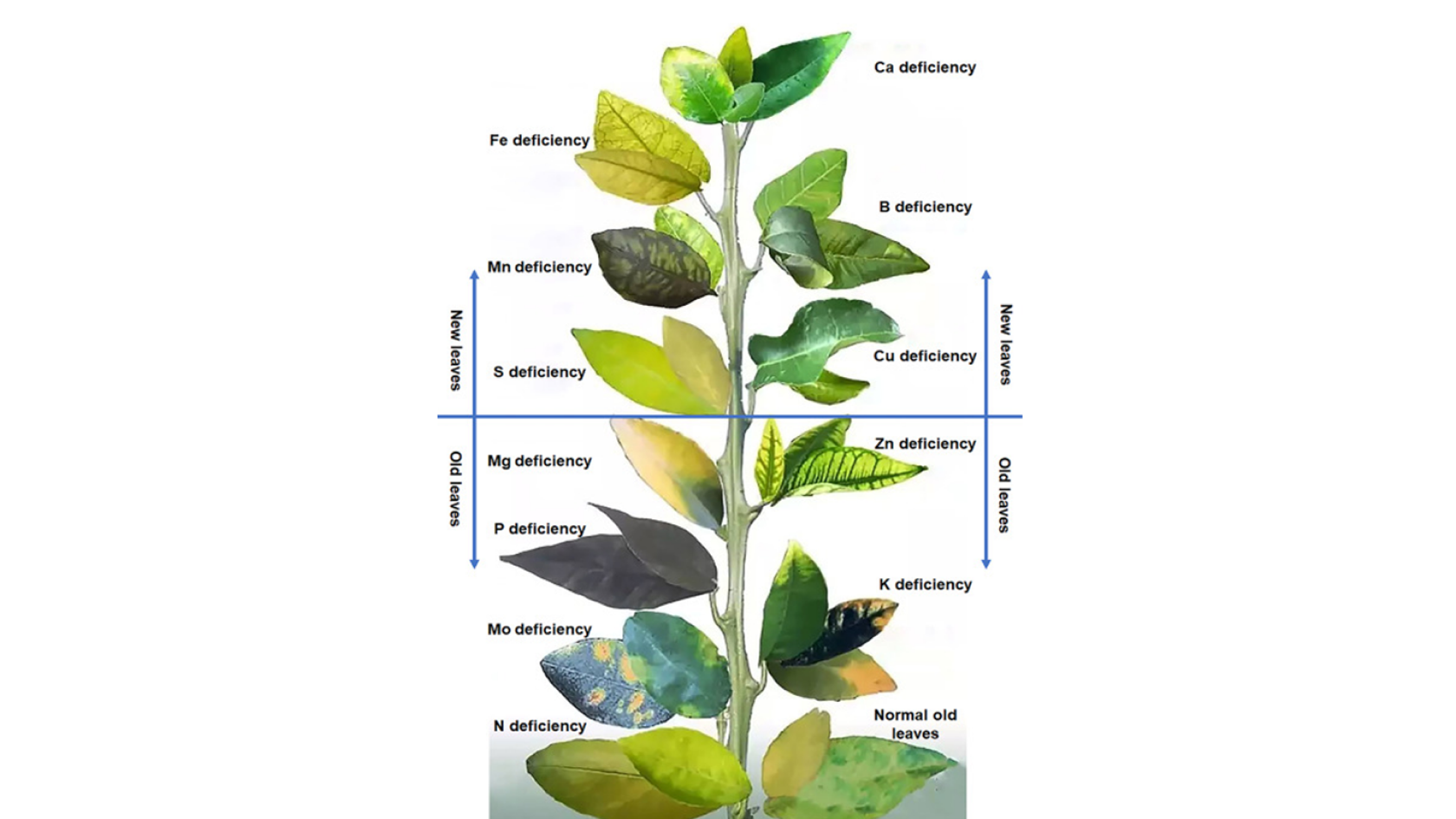
Once the role of the nutrients and their mobility in the plant is known, there are three more things to consider before moving on to the diagnosis. The first one is to make sure the symptoms are distributed equally over the field and not restricted to a specific region, indicating stress or pests. The second is the gradient of the signs. Nutritional deficiencies must appear in gradients, either from the top of the plant to the bottom or the other way around. And lastly, it is necessary to check for symmetry, since if there is a lack of a nutrient, the symptoms that happen on one side of the plant will be the same on the opposite side.
The traits of nutrient deficiency will vary from one crop to another, but here we will discuss some general deficiency signs of a few essential nutrients that can be seen on almost every crop. Visual Symptoms Of Nutrient Deficiency
 Nitrogen
This mineral is a component of the chlorophyll molecule and plays a role in many different vital
activities for the plant, which makes it fundamental for the crop’s growth and establishment. Given its
functions, the signs of nitrogen deficiency might show on the whole plant, as growth reduction and low
productivity, and on the old leaves, as they turn into a light-green colour which may evolve to
chlorosis.
Phosphorous
Everything the plant needs energy for will also require phosphorous. Responsible for energy storage and
transfer, when there is a lack of it in the plants, the signs will be a decrease in productivity,
dormant lateral gems, a smaller number of fruits and seeds and a delay in flowering. This mobile
nutrient might also announce its deficiency on the older leaves, through a yellowish colour or a blueish
green colour with brown spots, little gloss and a more acute foliar angle.
Nitrogen
This mineral is a component of the chlorophyll molecule and plays a role in many different vital
activities for the plant, which makes it fundamental for the crop’s growth and establishment. Given its
functions, the signs of nitrogen deficiency might show on the whole plant, as growth reduction and low
productivity, and on the old leaves, as they turn into a light-green colour which may evolve to
chlorosis.
Phosphorous
Everything the plant needs energy for will also require phosphorous. Responsible for energy storage and
transfer, when there is a lack of it in the plants, the signs will be a decrease in productivity,
dormant lateral gems, a smaller number of fruits and seeds and a delay in flowering. This mobile
nutrient might also announce its deficiency on the older leaves, through a yellowish colour or a blueish
green colour with brown spots, little gloss and a more acute foliar angle.
For corn specifically, phosphorous deficiency increases anthocyanin production, resulting in purplish staining of the leaves, which is a very characteristic deficiency trait for this crop. If the symptom appears, it means there is a need for fertilization. Fortunately, corn is in the i-Plant Nutrition database and can be selected for the creation of fertilizer plans when using the software.
 Potassium
If a crop isn’t getting enough potassium, it will probably lead to the tapering of the new leaves, and
on the old ones, a yellowing of the edges, that become brownish and necrotic, progressing then to the
center of the leaves. This happens because K has a high mobility in the plant, and is responsible for
many osmotic processes and enzymes activation.
Magnesium
This nutrient is an enzymatic activator, and a component of the chlorophyll molecule and cell wall. Its
deficiency shows through internal chlorosis of the old leaves and discoloration of the edges. These
signs will most likely be seen in sandy and acidic soils, in which magnesium is easily leached,
therefore not absorbed by the plant.
Potassium
If a crop isn’t getting enough potassium, it will probably lead to the tapering of the new leaves, and
on the old ones, a yellowing of the edges, that become brownish and necrotic, progressing then to the
center of the leaves. This happens because K has a high mobility in the plant, and is responsible for
many osmotic processes and enzymes activation.
Magnesium
This nutrient is an enzymatic activator, and a component of the chlorophyll molecule and cell wall. Its
deficiency shows through internal chlorosis of the old leaves and discoloration of the edges. These
signs will most likely be seen in sandy and acidic soils, in which magnesium is easily leached,
therefore not absorbed by the plant.
Even though it is mobile inside the plants, some crops, such as citrus might manifest symptoms on the young leaves as well, due to the high demand of magnesium by the fruits. Crops with a high potassium requirement, namely coffee and banana, may also have the same characteristic. That’s because Mg and K are absorbed through a double absorption mechanism, that can lead to a competition for the absorption site, and if too much potassium is applied to meet the demand, it will most likely interfere in the amount of magnesium the plant will take up.
The deficiency signs will differ depending on the nutrient and the crop, but in all of them, in order to confirm the lack of a nutrient, it is recommended to run a tissue test. If there is in fact a deficiency, the i-Plant Nutrition software will help you come up with a unique fertilizer plan, to ensure the health of the plants and increase the yields!