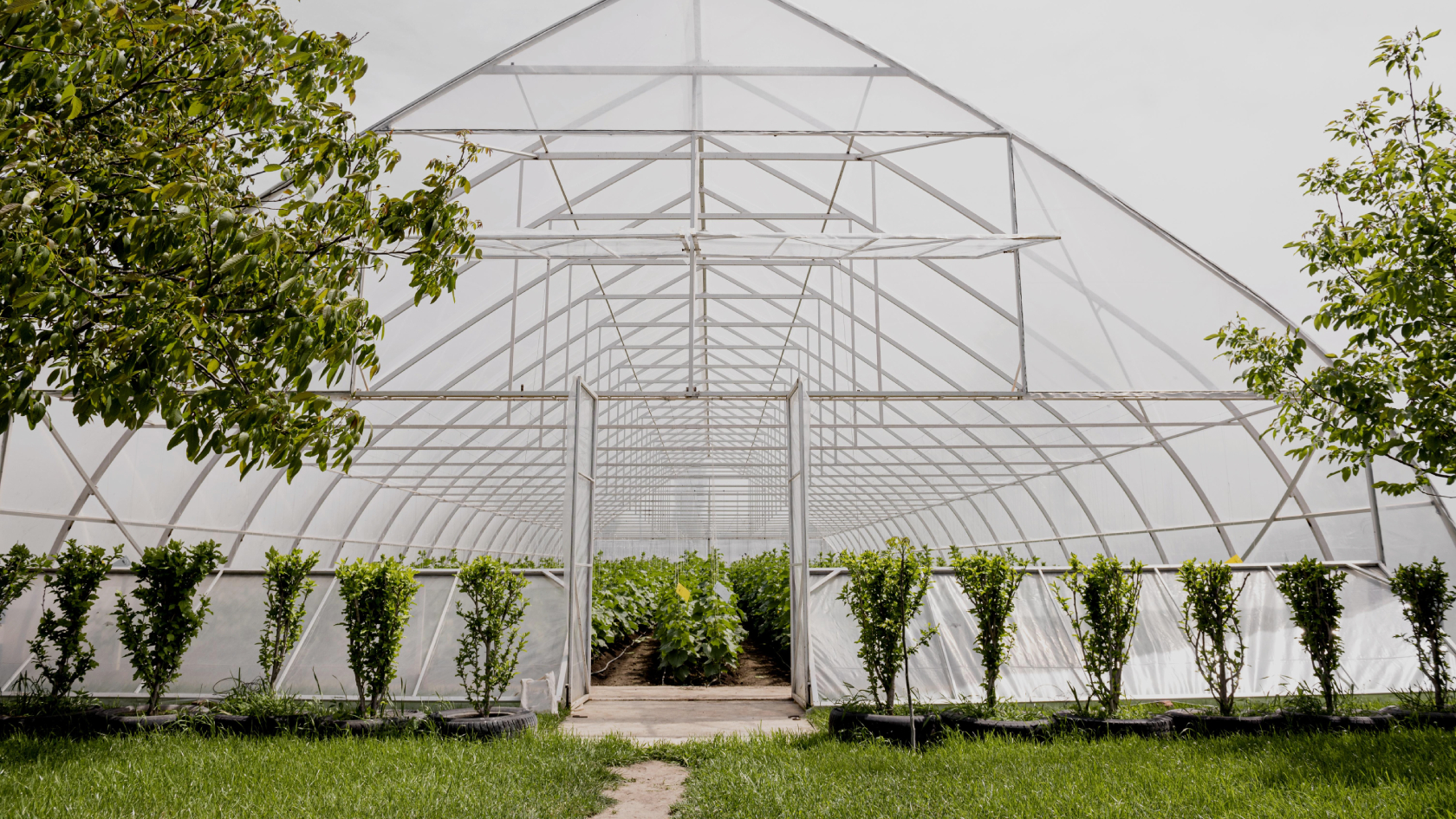
The sub-irrigation in protected environments such as greenhouses is a cyclic irrigation system that seeks to optimize the use of water, reinserting the nutrient solution throughout the development of the crop.
- How it works
For this to happen, the water is applied to the base of the production containers, and a pump located in the tank with the nutrient solution fills up the production table (or sub-irrigation bench), moving - through capillarity - the water with the solution from the base to the top of the containers, dampening the entire substrate. When the pump is turned off, gravity causes the nutrient solution to return to the initial tank, and so the production table will empty.
- Advantages
As in this system, the remaining nutrient solution is reused after being evaluated and having the necessary nutrients added, there is greater efficiency in the use of water and nutrients, and this waste reduction, besides saving such a scarce resource, also decreases environmental pollution, since these nutrients will not be dispersed in the environment.
The amount of nutrients supplied is also more accurate, since it is possible to reevaluate the nutrient solution frequently, which allows better growth control, shorter production time and greater uniformity.
Sub irrigation also enables the application of pesticides in the system and its automation, reducing respectively the damage by weeds and the need for manpower.
- Disadvantages
The system being a closed circuit also has its disadvantages, because since there is no leaching, the mineral salts accumulate at the top of the container. Fortunately, this does not cause stress to plants since their roots tend to grow more at the bottom of the container.
In addition, the reuse of water, if not done in the correct way, may favour the dissemination of water-borne phytopathogens.
As for the system itself, it can have a high initial cost, and due to its specificity, there is also a difficulty in reusing it for other functions in the property. This specificity coincides with the lack of technical data on the operation, which ends up driving producers away from choosing the use of sub-irrigation.
If you would like to know more about irrigation and fertigation systems and find out what is the best fit for you, contact us at i-Plant Nutrition and we will help you create the best strategy to increase your yield while saving resources.