1. How does this crop behave? The plant Glycine max, commonly known as soybean, is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) as one of the most important world crops. It is often grown as a rotation crop combined with cotton, maize and sorghum. The stages of this crop can be divided into initial, crop development, midseason and late season, during a total period from 100 to more than 130 days.
The commercialized parts of the soybean are the seeds. According to the last data, the yield varies between 1.5 and 2.5 tons/ha seed under rainfed conditions. Under irrigation, the yield can reach between 2.5 to 3.5 ton/ha seed. However, not only the water availability can affect the yield but also the nutrient availability. In i-Plant Nutrition, we calculate the best fertilization strategy for your soybean crop based on the characteristics of your field. Do not hesitate to use this tool to obtain higher benefits from your plantation.
 2. Know about common pests and diseases
Even if not all the pests and diseases observed in soybean crops are economically important, it is
interesting to know about their existence in order to prevent the plants from struggling with them.
Nowadays exists a large amount of genetically modified soybean to reinforce its drought tolerance or
pest and diseases resistance. According to the International Service for the Acquisition of
Agro-biotechnological Applications (ISAAA) in 2019, soybeans covered 48% of the world surface dedicated
to genetically modified crops. This makes it the first transgenic crop in the world, with 91.9 million
hectares cultivated. However, the legislation of some countries does not allow farmers to grow them. In
any case, we are mentioning in this article the pests and diseases affecting wild type plants, so please
take into account that some of them can be avoided by using resistant varieties.
2. Know about common pests and diseases
Even if not all the pests and diseases observed in soybean crops are economically important, it is
interesting to know about their existence in order to prevent the plants from struggling with them.
Nowadays exists a large amount of genetically modified soybean to reinforce its drought tolerance or
pest and diseases resistance. According to the International Service for the Acquisition of
Agro-biotechnological Applications (ISAAA) in 2019, soybeans covered 48% of the world surface dedicated
to genetically modified crops. This makes it the first transgenic crop in the world, with 91.9 million
hectares cultivated. However, the legislation of some countries does not allow farmers to grow them. In
any case, we are mentioning in this article the pests and diseases affecting wild type plants, so please
take into account that some of them can be avoided by using resistant varieties.
Although it is most common to observe symptoms caused by pathogens or pests first on the leaves, damage can be done to all parts of the plant, including roots, shoots, stems, pods and seeds. The least common case is that of problems that start at the root. Damage can be caused by various types of organisms such as bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and viruses. Pests also vary greatly, from insects to mammals. In any case, the most effective way to manage and control a disease is based on a proper diagnosis. That is why knowing the possible causes is key.
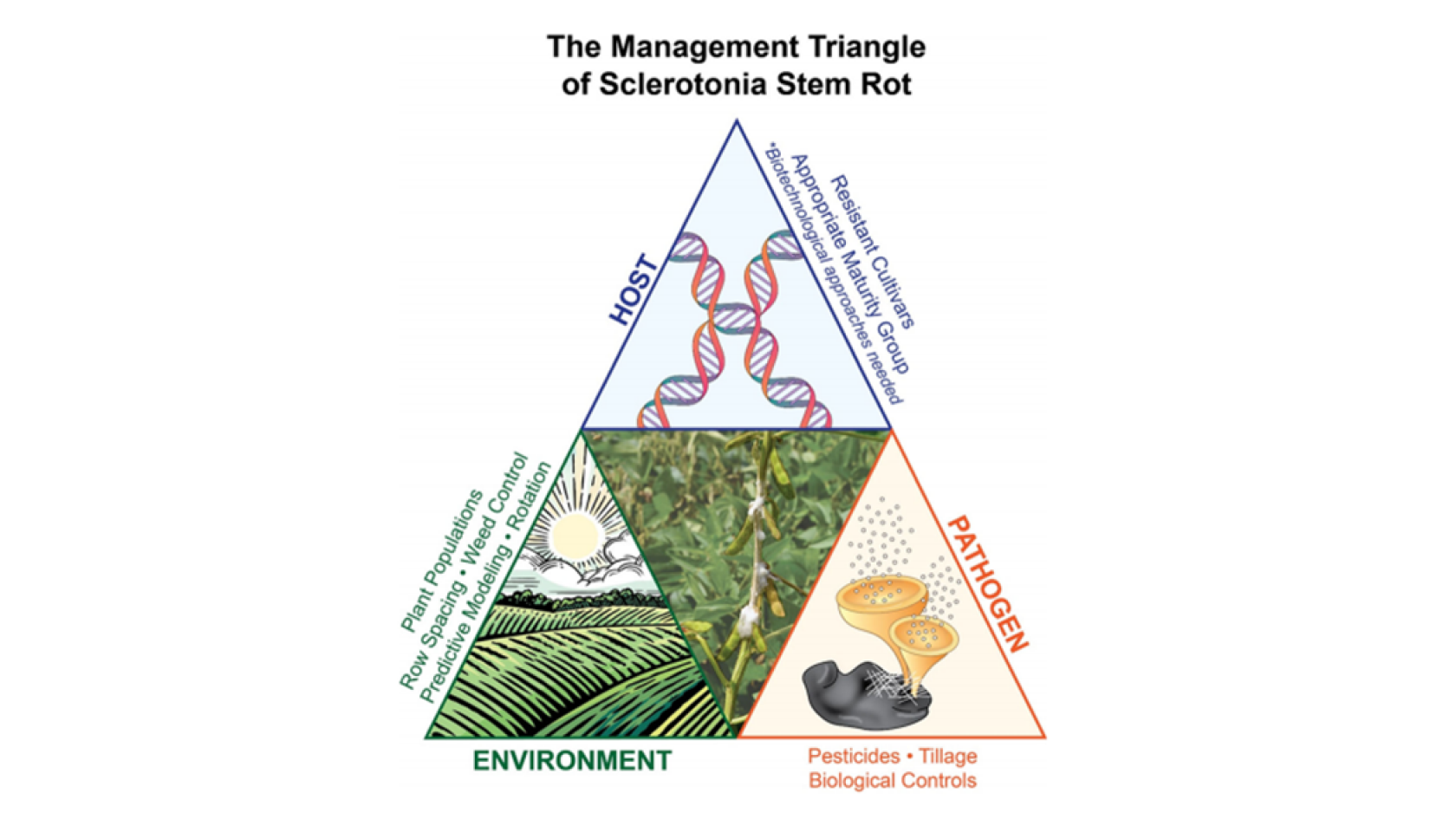
 2.1. Sclerotinia blocks the stem
flow
Sclerotinia stem rot (SSR) is a significant disease difficult to control, extended over 95 countries. It
is caused by the cosmopolitan fungal pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum that induce programmed cell death
in the host plant. This infection causes dramatic yield reductions, reducing seed number and weight
because of the enclosing of stems that disrupts the xylem and phloem flow. The strategies to deal with
this fungus can be addressed from three sides: by cultural practices to avoid the fungus development, by
using the appropriate soybean varieties according to the field location or with methods that attack
directly the pathogen.
2.1. Sclerotinia blocks the stem
flow
Sclerotinia stem rot (SSR) is a significant disease difficult to control, extended over 95 countries. It
is caused by the cosmopolitan fungal pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum that induce programmed cell death
in the host plant. This infection causes dramatic yield reductions, reducing seed number and weight
because of the enclosing of stems that disrupts the xylem and phloem flow. The strategies to deal with
this fungus can be addressed from three sides: by cultural practices to avoid the fungus development, by
using the appropriate soybean varieties according to the field location or with methods that attack
directly the pathogen.
 2.2. Direct to the seeds
Nothing can affect more the yield than pests and diseases attacking directly the seeds and pods. One of
these cases is the fungus Diaporthe longicola that causes the classic phomopsis seed decay (PSD) of
soybean. This infection can be observed by the nude eye because the seeds are often presenting chalky
white mold on their surface. Even if the currently available fungicide seed treatments seem to be quite
effective against this fungus, it is recommended to control the presence of it and as fast as possible
eradicate the infected plants.
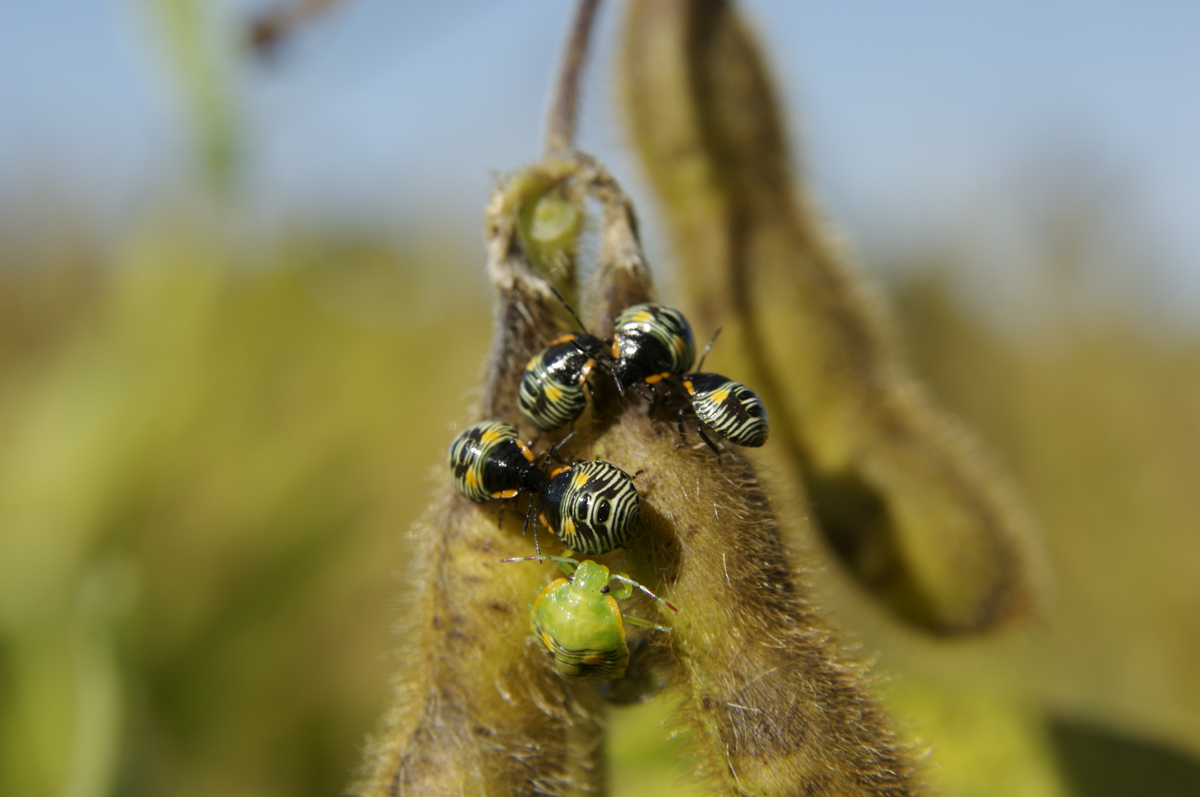
2.3. The always unwelcome aphids
Aphids are approximately 1,5 mm insects that needle the soybean plants to extract plant juices using its
sucking structures. Even if they are so small, their reproduction tax is so fast that a plant can be
rapidly infected by a large number of them, blocking the stem flow. This disease is not easy to get rid
of without using proper insecticides. In addition, the damage they cause on the stems are sometimes the
entrance of bacteria, virus and fungus and amplified the damage. In North America, the registered data
shows that over 30% of the yield is lost on average when this insect is present.
3. A general overview
Two very common diseases and a pest were spotted in this article because its presence has been observed
all around the world as causing a large drop in yield. Did you find any infection signals in your
plants? Do not hesitate to upload it at the i-Plant Nutrition forum to get the best advice from our
experts and the community. Make sure you follow our articles to find more useful information and obtain
the highest production from your field.
2.2. Direct to the seeds
Nothing can affect more the yield than pests and diseases attacking directly the seeds and pods. One of
these cases is the fungus Diaporthe longicola that causes the classic phomopsis seed decay (PSD) of
soybean. This infection can be observed by the nude eye because the seeds are often presenting chalky
white mold on their surface. Even if the currently available fungicide seed treatments seem to be quite
effective against this fungus, it is recommended to control the presence of it and as fast as possible
eradicate the infected plants.
2.3. The always unwelcome aphids
Aphids are approximately 1,5 mm insects that needle the soybean plants to extract plant juices using its
sucking structures. Even if they are so small, their reproduction tax is so fast that a plant can be
rapidly infected by a large number of them, blocking the stem flow. This disease is not easy to get rid
of without using proper insecticides. In addition, the damage they cause on the stems are sometimes the
entrance of bacteria, virus and fungus and amplified the damage. In North America, the registered data
shows that over 30% of the yield is lost on average when this insect is present.
3. A general overview
Two very common diseases and a pest were spotted in this article because its presence has been observed
all around the world as causing a large drop in yield. Did you find any infection signals in your
plants? Do not hesitate to upload it at the i-Plant Nutrition forum to get the best advice from our
experts and the community. Make sure you follow our articles to find more useful information and obtain
the highest production from your field.